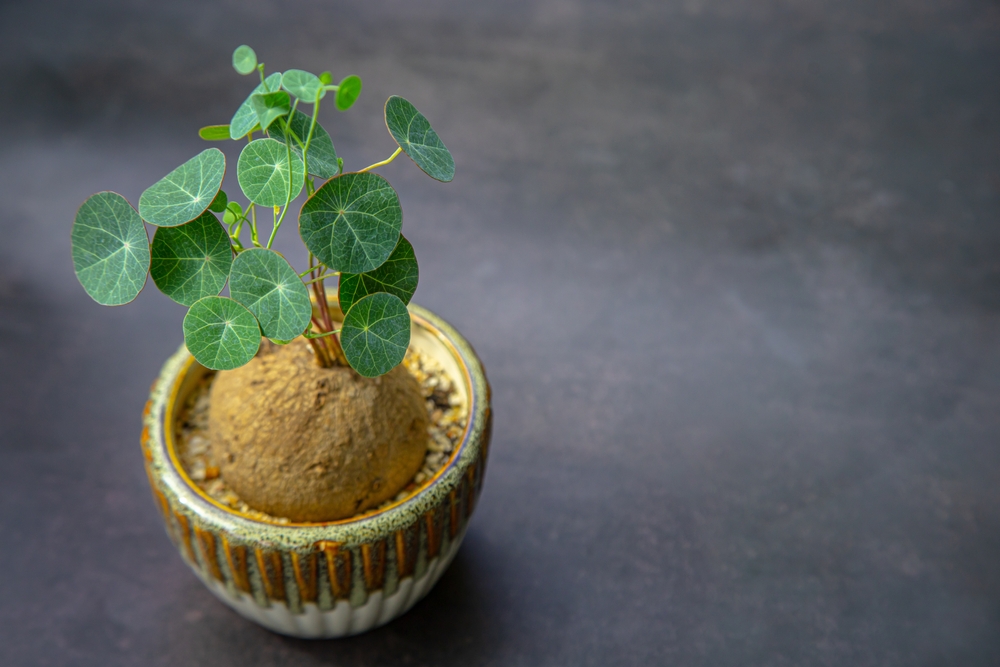
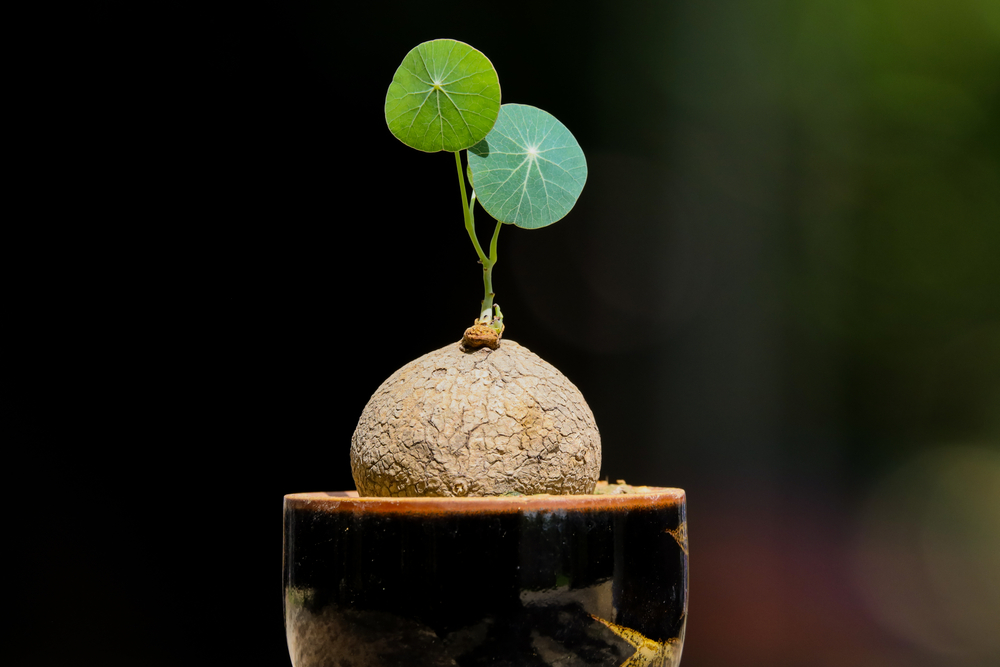
As house plants become common in many house decor plans, choosing a trendy house plant is also necessary. Stephania erecta can be the true definition of beauty and trends in the house plant world. It is loved because of its unique potato-like structure and simple care requirement.
| Botanical Name | Stephania erecta |
| Common Name | Stephania |
| Plant Type | Perennial |
| Flower Color | Yellow small flowers |
| Size When Mature | 36 inches tall and 6 to 7 inches wide |
| Bloom Time | In spring |
| Sun Requirements | Partial sun |
| USDA Hardiness Zones | Zone 10 and 11 |
| Soil PH Range | 6.5 to 7.0 |
| Soil Type | Slightly acidic, well-draining |
| Water Needs | Low watering |
| Native Area | Thailand |
Stephania erecta can add a unique green hue to your house décor, especially when you provide it with ideal growing conditions, and well-designed climbing space.
Whether you are new to nurturing houseplants or want to add a fresh taste to your wide range of houseplants, you can confidently try the Stephania erecta. Keep reading to learn more about the Stephania erecta and how to care for it.
What you need to know about Stephania erecta
Stephania erecta, also known as Stephania Pierre, is native to Thailand and is commonly identified by its large woody bulb known as a caudex. From the caudex (potato part) sprouts tall, slender, straight stalks. The stalks are classified as the erecta part of the plant.
At the top part of the stalks, shield-shaped deep-green leaves growing up to 2 inches wide are usually arranged in a whimsical pattern. The leaf pattern makes the plant attractive and intriguing for any indoor ambiance.
Notably, Stephania erecta can and do produce yellowish flowers in spring, but this will not happen in all seasons. However, if it fails to bloom at any given season, it will likely bloom in the next spring season.
Stephania erecta takes several years to mature, with some plants taking up to 20 years to fully mature. At maturity, the plant will have grown to about three feet high. Its width is usually about 6 to 7 inches.
Overall, growing Stephania erecta is simple because all you need is a good potting mix and the plant tuber or seed. In ideal conditions, it will remain evergreen, adding interest and color to your living space.
NOTE: Even though the Stephania erecta appears more like a potato, it should only remain attractive to the eyes and never to the stomach. It is toxic and should not be eaten.
How to care for Stephania erecta
Here is everything you need to know about growing and caring for a thriving Stephania erecta.
Light requirements
Like most house plants, Stephania erecta grows well in bright but indirect sunlight. However, it can still grow when exposed to moderate direct sunlight. It is important to note that the direct summer scorching sunlight can damage the leaves of Stephania erecta. In contrast, inadequate light makes them leggy.
Place your plant at a spot where it receives at least 4 to 6 hours of indirect yet bright sunlight. A window with curtains or blinds to filter light can be an ideal place. During the cold season, you can use heat mats and grow lights to provide the plant with adequate light and warmth. You can move the plant away from the window in winter to lower the risks of being affected by extreme coldness.
Water and soil need
A sand-based potting mix can do well for the Stephania erecta plant. Cacti and succulent soil can also be good for pots where you want to plant Stephania erecta. The soil should be well draining and have a pH ranging from 6.5 to 7.
Water the plant at least once every week after planting, and once it establishes, only water when half the potting soil is dry. Avoid overwatering because this plant doesn’t tolerate excess moisture well. Use tepid water when watering the plant to save the roots from the shock of either hotness or coldness brought about by water.
Temperature requirements
Stephania erecta ideal growing temperature is 60 to 80 degrees Fahrenheit. It grows well in USDA zones 10 and 11.
Fertilizer requirement
Fertilizer is not a necessary facet for the care of Stephania erecta. However, you can apply liquid fertilizer once a month during the active spring growing season. While fertilizing, take the appropriate measurements because too much fertilizer will damage the plant.
Common disease
The most common disease that affects Stephania erecta is root rot. It is caused by overwatering or planting it in poorly drained soils. To safeguard your houseplant, avoid overwatering the plant and always use the right potting soil mix.
Propagating
Propagation can be done through bulbs and seeds. Put the bulbs or seeds in water and keep them in a warm dark place for about 24 hours. Plant the seed or bulb in cacti soil while ensuring that just 0.2 inches of the plant get deep into the soil. The remaining part should be on top of the soil. Water weekly to help the plant develop roots.